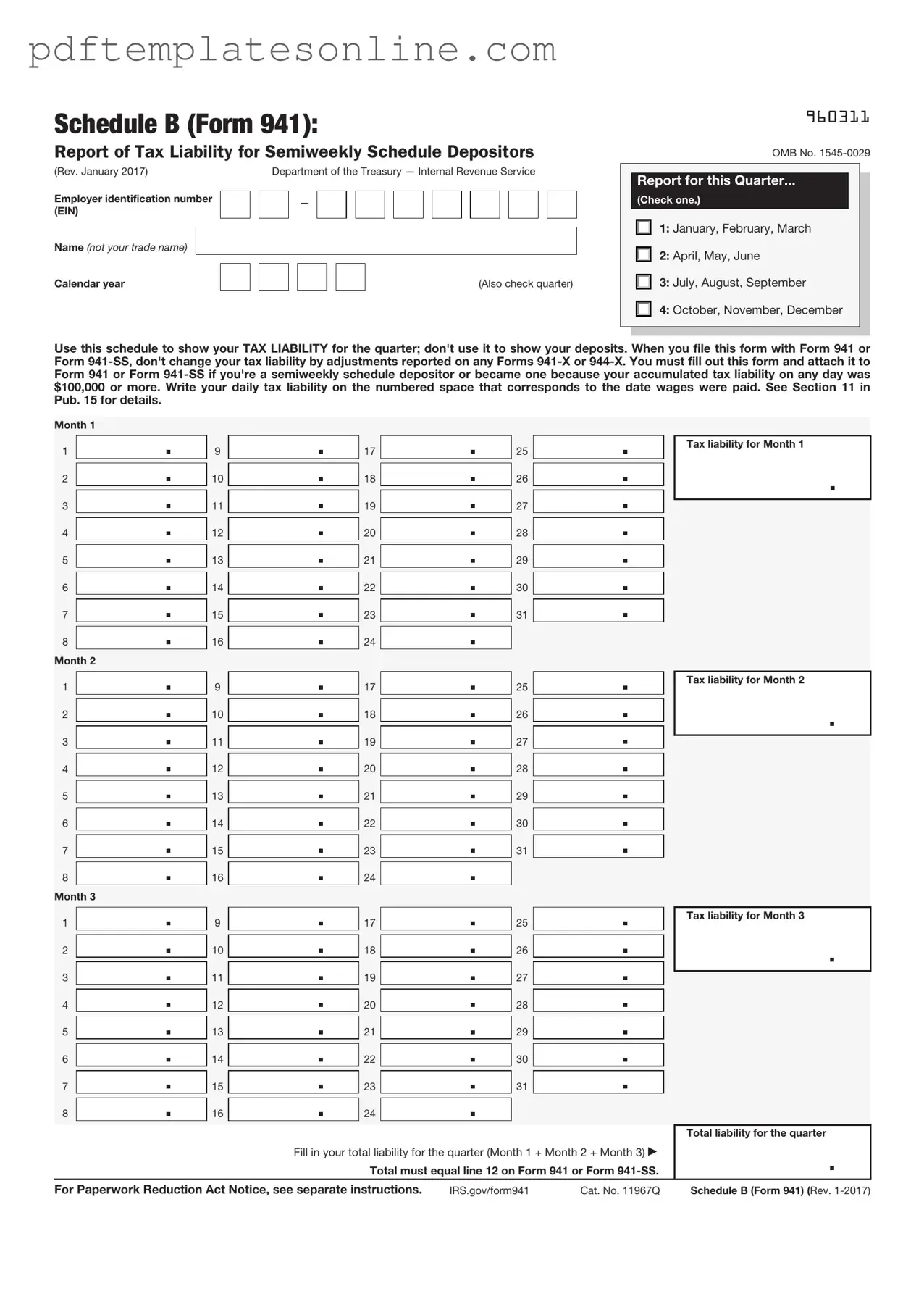
Blank IRS Schedule B 941 Form
Key takeaways
When dealing with the IRS Schedule B (Form 941), it is essential to understand its purpose and how to fill it out correctly. Here are some key takeaways to keep in mind:
- Purpose of Schedule B: This form is used to report the tax liability for employment taxes. It helps the IRS track your payroll tax obligations on a quarterly basis.
- Filing Frequency: Schedule B must be filed quarterly along with Form 941. Ensure that you submit it by the due date to avoid penalties.
- Accurate Reporting: It is crucial to report the correct amounts for wages, tips, and other compensation. Mistakes can lead to discrepancies and potential audits.
- Tax Liability Calculation: The form requires you to calculate your total tax liability for each month of the quarter. This includes any adjustments for prior periods.
- Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of all payroll transactions. This documentation will support the figures reported on Schedule B and is vital in case of an audit.
By understanding these key aspects, you can navigate the requirements of Schedule B with greater confidence and accuracy.
Common mistakes
Filling out the IRS Schedule B (Form 941) can be a straightforward process, but many individuals make common mistakes that can lead to complications. One frequent error is failing to report all wages and tips accurately. It's essential to include all taxable wages and tips paid to employees during the quarter. Omitting any amounts can result in discrepancies and potential penalties.
Another mistake involves incorrect calculations of taxes withheld. Individuals sometimes miscalculate the amount of federal income tax withheld from employees' paychecks. Ensuring that these figures are accurate is crucial, as they directly impact the employer's tax liability.
Some filers also overlook the importance of reconciling the amounts reported on Form 941 with their payroll records. Discrepancies between these documents can raise red flags with the IRS. It's advisable to double-check that the numbers match before submission.
In addition, many people forget to sign and date the form. A missing signature can lead to delays in processing and may even result in penalties. Always remember to complete this final step to validate the submission.
Not using the correct version of the form is another common error. The IRS updates forms periodically, and using an outdated version can lead to complications. Always ensure you are using the most current version available on the IRS website.
Another mistake is submitting the form late. Employers must file Form 941 quarterly, and failing to meet the deadline can result in penalties. Setting reminders can help ensure timely submissions.
Some individuals also misinterpret the instructions provided by the IRS. It is essential to read the guidelines thoroughly, as they offer specific directions on how to complete the form correctly. Misunderstanding these instructions can lead to errors.
Additionally, people sometimes fail to keep copies of their submitted forms. Retaining copies is important for record-keeping and can be invaluable if questions arise in the future regarding the submitted information.
Lastly, not seeking professional help when needed can lead to mistakes. If there is uncertainty about how to fill out the form correctly, consulting a tax professional can provide clarity and ensure compliance with IRS regulations.
Misconceptions
Understanding the IRS Schedule B (Form 941) is crucial for employers. However, several misconceptions can lead to confusion. Here are six common misunderstandings:
-
Schedule B is only for large employers.
This is not true. All employers who are required to file Form 941 must complete Schedule B if they have a tax liability of $100,000 or more during the lookback period.
-
Schedule B is optional.
In fact, if you meet the criteria for filing it, completing Schedule B is mandatory. Failing to do so can result in penalties.
-
Schedule B is only for reporting employee wages.
While it does include wages, it primarily focuses on reporting tax liabilities and the timing of tax deposits.
-
Only full-time employees are considered for Schedule B.
This is incorrect. All employees, regardless of their work status, contribute to the calculations on Schedule B.
-
Filing Schedule B guarantees that I won’t be audited.
There’s no guarantee against audits. Filing accurately can help reduce the likelihood, but it does not eliminate the possibility.
-
Schedule B can be filed at any time.
Schedule B must be filed with your quarterly Form 941. Timeliness is crucial to avoid penalties.
By clarifying these misconceptions, you can ensure compliance and avoid unnecessary complications with the IRS.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the IRS Schedule B (Form 941), it’s essential to approach the process with care. Here’s a straightforward list of things to do and avoid to ensure accuracy and compliance.
- Do double-check your employer identification number (EIN) to ensure it’s correct.
- Do accurately report the total wages paid to employees during the quarter.
- Do include all applicable tax periods when reporting tax liabilities.
- Do keep a copy of the completed form for your records.
- Don’t forget to sign and date the form before submitting it.
- Don’t leave any fields blank; if a question doesn’t apply, indicate that with “N/A.”
- Don’t mix up the reporting periods; each quarter has specific requirements.
- Don’t submit the form late; ensure it’s filed by the deadline to avoid penalties.
Other PDF Forms
Rosebud, South Dakota - Ensure that the application is signed before a notary public, as per legal requirement.
For those dealing with estates that fall under the specified threshold, the California Small Estate Affidavit form not only streamlines the legal process but also serves as a vital resource. By utilizing this form, individuals can ensure a smoother transition of assets, making it an excellent option for heirs and beneficiaries. For more information and resources, visit California PDF Forms.
Gun License Price - The form necessitates details of the current firearm owner, including their identification information.
Create Own Invoice - Create itemized invoices to clarify charges for your clients.
Detailed Guide for Writing IRS Schedule B 941
After gathering the necessary information, you are ready to fill out the IRS Schedule B (Form 941). This form is essential for reporting your tax obligations accurately. Follow the steps below to complete it correctly.
- Begin by entering your name, business name, and Employer Identification Number (EIN) at the top of the form.
- In the section for the reporting period, specify the quarter you are filing for, such as January to March, April to June, July to September, or October to December.
- List all employees who received wages during the reporting period. Include their names and Social Security numbers.
- Indicate the total number of employees who received wages during the quarter in the appropriate box.
- Calculate the total wages paid to employees during the quarter and enter that amount in the designated field.
- Document any adjustments for fractions of cents, sick pay, or tips that were not reported as wages.
- Review the form for accuracy and ensure all required fields are completed.
- Sign and date the form to certify that the information provided is true and accurate.
- Submit the completed form to the IRS by the due date, either electronically or by mail.